Introduction
Overview
This User’s Guide covers the models listed below:
• NWA50AX
• NWA90AX
• NWA55AXE
• NWA50AX PRO
• NWA90AX PRO
The Zyxel Device can be managed in one of the following methods: remote management through Nebula Control Center (NCC) or local management in Standalone Mode. The Zyxel Device runs in standalone mode by default, but it is recommended to use NCC management if it is available for your device. For more information about Access Point (AP) management, see Management Mode.
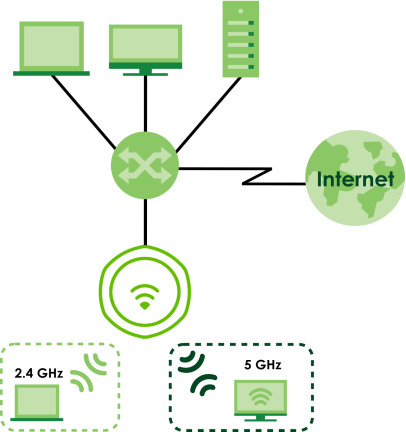
Use the Zyxel Device to set up a WiFi network with other IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax compatible devices in either 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks or both at the same time.
When two or more APs are interconnected, this network is called a Wireless Distribution System (WDS). See Zyxel Device Roles for more information on root and repeater APs and how to set them up.
The screens you see in the web configurator may be different depending on the Zyxel Device model you’re using.
Zyxel Device Product Feature Comparison
The following table lists the features of the Zyxel Device.
Features | NWA50ax | NWA90ax | NWA55axe |
|---|---|---|---|
Supported WiFi Standards | IEEE 802.11a IEEE802.11b IEEE 802.11g IEEE 802.11n IEEE 802.11ac IEEE802.11ax | IEEE 802.11a IEEE802.11b IEEE 802.11g IEEE 802.11n IEEE 802.11ac IEEE802.11ax | IEEE 802.11a IEEE802.11b IEEE 802.11g IEEE 802.11n IEEE 802.11ac IEEE802.11ax |
Multi-Link Operation (MLO) | No | No | No |
Supported Frequency Bands | 2.4 GHz 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz 5 GHz |
Supported Channel Width | 2.4G: 20/40 MHz 5G: 20/40/80 MHz | 2.4G: 20/40 MHz 5G: 20/40/80 MHz | 2.4G: 20/40 MHz 5G: 20/40/80 MHz |
Available Security Modes | None / Enhanced-open / WEP / WPA2-MIX-Personal / WPA3-Personal | None / Enhanced-open / WEP / WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -Personal & Enterprise | None / Enhanced-open / WEP / WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -Personal & Enterprise |
Number of SSID Profiles | 64 | 64 | 64 |
Number of WiFi Radios | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Security Profile Radius Settings | No | Yes | Yes |
Security Profile Enterprise Authentication Settings | No | Yes | Yes |
Rogue AP Detection | Yes | Yes | Yes |
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) - Root AP & Repeater Modes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Wireless Bridge | No | No | Yes |
Layer-2 Isolation | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Supported PoE Standards | IEEE 802.3at | IEEE 802.3at | IEEE 802.3at |
Power Detection | No | No | No |
External Antennas | No | No | Yes |
Internal Antennas | Yes | Yes | No |
Console Port | 4-Pin Serial | 4-Pin Serial | No |
Reset button | Yes | Yes | No |
LED Locator | Yes | Yes | No |
LED Suppression | Yes | Yes | Yes |
APC (AP Controller) Discovery | No | No | No |
NCC Discovery | Yes | Yes | Yes |
802.11r Fast Roaming Support | Yes | Yes | Yes |
802.11k/v Assisted Roaming | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Ethernet Storm Control | No | No | No |
Grounding | No | No | No |
Power Jack | Yes | Yes | No |
Maximum number of log messages | 512 event logs | ||
Latest Firmware Version Supported | 7.10 | 7.10 | 7.10 |
Features | NWA50ax PRO | NWA90ax PRO |
|---|---|---|
Supported WiFi Standards | IEEE 802.11a IEEE802.11b IEEE 802.11g IEEE 802.11n IEEE 802.11ac IEEE802.11ax | IEEE 802.11a IEEE802.11b IEEE 802.11g IEEE 802.11n IEEE 802.11ac IEEE802.11ax |
Multi-Link Operation (MLO) | No | No |
Supported Frequency Bands | 2.4 GHz 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz 5 GHz |
Supported Channel Width | 2.4G: 20/40 MHz 5G: 20/40/80/160 MHz | 2.4G: 20/40 MHz 5G: 20/40/80/160 MHz |
Available Security Modes | None / Enhanced-open / WEP / WPA2-MIX-Personal / WPA3-Personal | None / Enhanced-open / WEP / WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -Personal & Enterprise |
Number of SSID Profiles | 64 | 64 |
Number of WiFi Radios | 2 | 2 |
Security Profile Radius Settings | No | Yes |
Security Profile Enterprise Authentication Settings | No | Yes |
Rogue AP Detection | Yes | Yes |
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) - Root AP & Repeater Modes | Yes | Yes |
Wireless Bridge | No | No |
Layer-2 Isolation | Yes | Yes |
Supported PoE Standards | IEEE 802.3at | IEEE 802.3at |
Power Detection | No | No |
External Antennas | No | No |
Internal Antennas | Yes | Yes |
Console Port | 4-Pin Serial | 4-Pin Serial |
Reset Button | Yes | Yes |
LED Locator | Yes | Yes |
LED Suppression | Yes | Yes |
APC (AP Controller) Discovery | No | No |
NCC Discovery | Yes | Yes |
802.11r Fast Roaming Support | Yes | Yes |
802.11k/v Assisted Roaming | Yes | Yes |
Ethernet Storm Control | No | No |
Grounding | No | No |
Power Jack | Yes | Yes |
Maximum number of log messages | 512 event logs | |
Latest Firmware Version Supported | 7.10 | 7.10 |
Zyxel Device Roles
This section describes some of the different roles that your Zyxel Device can take up within a network. Not all roles are supported by all models (see Zyxel Device Product Feature Comparison). The Zyxel Device can serve as a:
• Access Point (AP) – This is used to allow WiFi clients to connect to the Internet.
• Radio Frequency (RF) monitor – If your Zyxel Device supports rogue APs detection, it can serve as an RF monitor and searches for rogue APs to help eliminate network threats. An RF monitor can simultaneously act as an AP.
• Root AP – A root AP connects to the gateway or switch through a wired Ethernet connection and has wireless repeaters connected to it to extend its range.
• WiFi Repeater – A WiFi repeater wirelessly connects to a root AP and extends the network’s wireless range. A wireless repeater can also be a wireless bridge that connects to a root AP and extends the network to wired client devices.
If a client (D) tries to set up his own AP (R) with weak security settings, the network becomes exposed to threats. The RF monitor (M) scans the area to detect all APs, which can help the network administrator discover these rogue APs.
Zyxel Device Application in a Network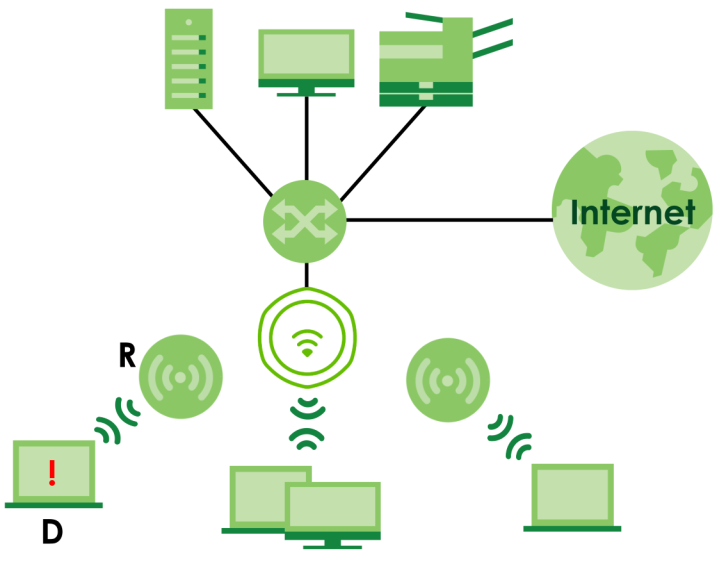

Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) is a network system that allows you to distribute the network to areas that require Internet connections. You can extend your network to unreachable areas with wireless repeaters.
The following figure shows you how to create a secure WDS with two wireless repeaters. The root AP (Y) is connected to a network with Internet access and has wireless repeaters (X and Z) connected to it to expand the WiFi network’s range. Clients (A and B) can access the wired network through the wireless repeaters (X and Z) and/or root AP.
Wireless Distribution System Network Example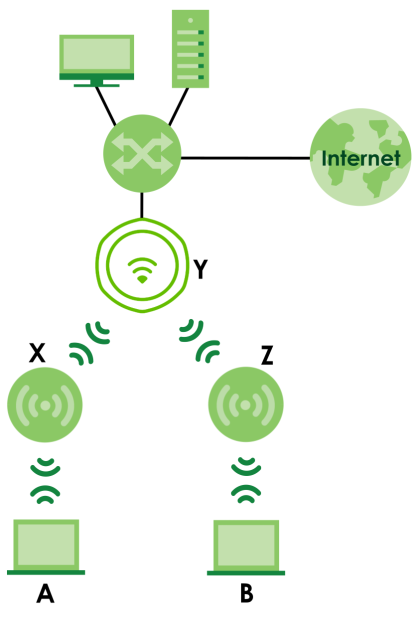

The Zyxel Device can also serve as a wireless bridge in Repeater mode. A wireless bridge connects two wired networks through a wireless connection. When the Zyxel Device is connected to a root AP, enable wireless bridge to allow traffic through the Ethernet port on the Zyxel Device to a wired network. Check Zyxel Device Product Feature Comparison for models that support wireless bridge.
The following figure shows an example of a WDS with a repeater acting as a wireless bridge. The root AP (X) is connected to a network with Internet access. The wireless repeater (Y) is connected to the root AP (X) to expand the network. Clients (A and B) are connected to the wireless repeater through the switch/gateway/router (G). They can access the network with the extended wired network the wireless bridge (wireless repeater) provides.
Wireless Bridge Network Example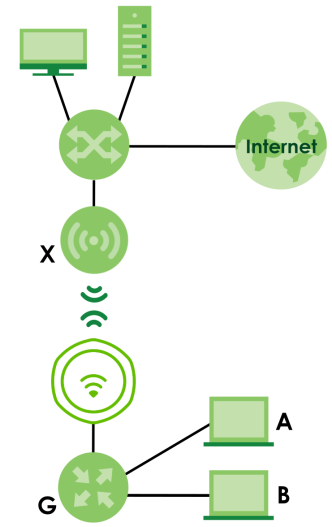

Access Point (AP)
The Zyxel Device can receive connections from WiFi clients and pass their data traffic through to the Zyxel Device to be managed (or subsequently passed on to an upstream gateway for managing).
In AP Mode, the Zyxel Device is connected to a broadband modem with Internet access and provides a WiFi network for users to use their notebooks or computers to wirelessly access the Internet.
AP Mode Application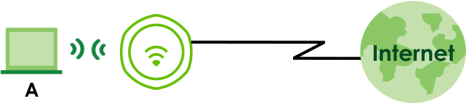

Root AP
The Zyxel Device acts as an AP and also supports the WiFi connections with other APs (in repeater mode) to form a WDS to extend its WiFi network.
In Root AP mode, you can have multiple SSIDs active for regular WiFi connections and one SSID (WDS SSID) for the connection with a repeater. WiFi clients can use either SSID to associate with the Zyxel Device in Root AP mode. A repeater must use the repeater SSID to connect to the Zyxel Device in Root AP mode. See Overview for more details.
When the Zyxel Device is in Root AP mode, repeater security between the Zyxel Device and other repeaters is independent of the security between the WiFi clients and the AP or repeater. When repeater security is enabled, both APs and repeaters must use the same pre-shared key. See AP Management and WDS Profile for more details.
Unless specified, the term “security settings” refers to the traffic between the WiFi clients and the AP. At the time of writing, repeater security is compatible with the Zyxel Device only.
WiFi Repeater
The Zyxel Device can establish a WiFi connection with other APs (in either Root AP or Repeater mode) to form a WDS.
Using Repeater mode, your Zyxel Device can extend the range of the WLAN. In the figure below, the Zyxel Device in Repeater mode (Z) has a WiFi connection to the Zyxel Device in Root AP mode (X) which is connected to a wired network and also has a WiFi connection to another Zyxel Device in Repeater mode (Y) at the same time. Z acts as a repeater that forwards traffic between associated WiFi clients and the wired LAN. Y acts as a WiFi bridge (repeater with WDS wireless bridging enabled) that forwards traffic between wired clients and the wired LAN. Clients A and B access the AP and the wired network behind the AP through repeaters Z and Y.
Repeater Application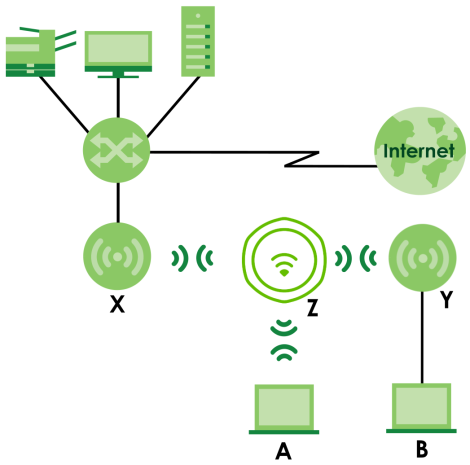

When the Zyxel Device is in Repeater mode, repeater security between the Zyxel Device and other repeater is independent of the security between the WiFi clients and the AP or repeater. When repeater security is enabled, both APs and repeaters must use the same pre-shared key. See AP Management and WDS Profile for more details.
For NCC managed devices, you only need to enable AP Smart Mesh to automatically create WiFi links between APs. See the NCC User’s Guide for more details.
Radio Frequency (RF) Monitor
The Zyxel Device supports Rogue AP Detection (see Rogue AP). Rogue AP Detection allows the Zyxel Device to be set to work as an RF monitor to discover nearby Access Points. The information it obtains from other APs is used to tag possible rogue APs and friendly APs. The Zyxel Device can still work as an AP while it scans the environment for wireless signals.
Sample Feature Applications
This section describes some possible scenarios and topologies that you can set up using your Zyxel Device.
MBSSID
A Basic Service Set (BSS) is the set of devices forming a single WiFi network (usually an access point and one or more WiFi clients). The Service Set IDentifier (SSID) is the name of a BSS. In Multiple BSS (MBSSID) mode, the Zyxel Device provides multiple virtual APs, each forming its own BSS and using its own individual SSID profile.
You can configure multiple SSID profiles, and have all of them active at any one time.
You can assign different wireless and security settings to each SSID profile. This allows you to compartmentalize groups of users, set varying access privileges, and prioritize network traffic to and from certain BSSs.
To the WiFi clients in the network, each SSID appears to be a different access point. As in any WiFi network, clients can associate only with the SSIDs for which they have the correct security settings.
For example, you might want to set up a WiFi network in your office where Internet telephony (VoIP) users have priority. You also want a regular WiFi network for standard users, as well as a ‘guest’ WiFi network for visitors. In the following figure, VoIP_SSID users have QoS priority, SSID01 is the WiFi network for standard users, and Guest_SSID is the WiFi network for guest users. In this example, the guest user is forbidden access to the wired Local Area Network (LAN) behind the AP and can access only the Internet.
Multiple BSSs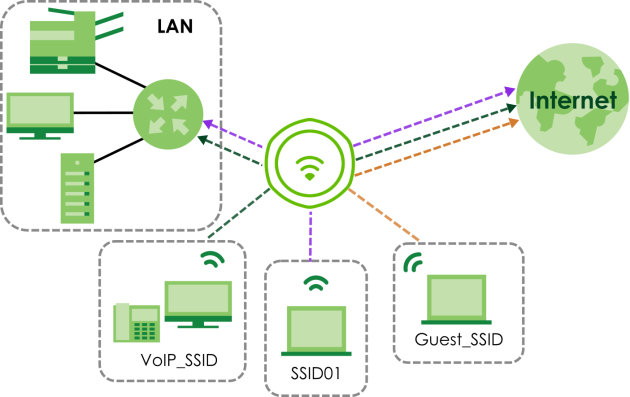

Dual-Radio
Some of the Zyxel Device models are equipped with dual WiFi radios. This means you can configure different WiFi networks on the 2.4G and 5G bands to operate simultaneously.
You could use the 2.4 GHz band for regular Internet surfing and downloading while using the 5 GHz band for time sensitive traffic like high-definition video, music, and gaming.
Dual-Radio Application